what is the source of energy for the water cycle and carbon cycle to occur
Climate and Earth's Energy Balance
Part A: Solar Energy and the H2o Cycle
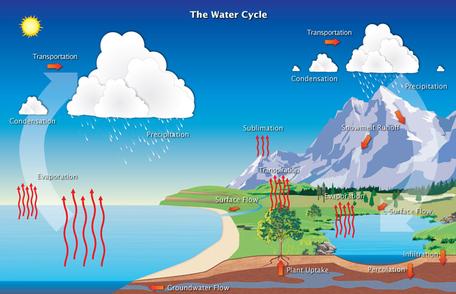
Simplified hydrologic, or water cycle. Click image for larger view. Source: NWS JetStream
To showtime the investigation of Earth's free energy residuum, you will begin past taking an in-depth look at a familiar process known as the water cycle. Earth'southward water supply is recycled in a continuous process known as the water, or hydrologic hydrologic bike: the process of evaporation, vertical and horizontal transport of vapor, condensation, precipitation, and the flow of water from continents to oceans. , cycle. Water molecules continuously move from location to location in this cycle. The water cycle is important to weather and climate and, ultimately, to all life on Earth.
The h2o bicycle is driven primarily by the energy from the lord's day. This solar energy drives the cycle by evaporating water from the oceans, lakes, rivers, and fifty-fifty the soil. Other water moves from plants to the atmosphere through the process of transpiration. Equally liquid water evaporates or transpires, it forms water vapor and clouds, where water droplets somewhen gain plenty mass to fall dorsum to Earth equally precipitation. The precipitation then becomes run-off or ground water, and works its way—over diverse timescales—dorsum into the surface reservoirs. The h2o bike is substantially a closed system, meaning that the volume of water that is in the hydrosphere today is the same corporeality of water that has always been present in the World system.
Begin this lab by watching the post-obit brusk NASA animation demonstrating the path of i water molecule through the water wheel. While watching the animation, make a list and continue runway of all the places that the molecule travels. Notation: In the NASA animation, the depiction of the water reservoirs, such as hush-hush aquifers aquifers: underground water reservoirs that form in the spaces and cracks between rocks, sand, or gravel, where water travels relatively hands. , has been simplified to evidence the molecule pathways.
Courtesy of NASA/Goddard Space Flight Heart Source: NASA Click Water Cycle Animation to view the animation in a new window.
As discussed earlier, the water cycle not only redistributes h2o around Earth, it also absorbs and redistributes solar energy between locations. Latent heating Latent heating: the energy required to change a substance to a college state of affair (solid to liquid, or liquid to gas). This same energy is released from the substance when the change of state is reversed (gas to liquid, or liquid to solid). of Earth's atmosphere occurs as energy, primarily from the sun, causes liquid water to transform to some other phase. As this occurs, liquid water absorbs energy, causing it to evaporate and form water vapor. The procedure of evaporation absorbs tremendous amounts of incoming solar free energy. Through the procedure of latent heating, free energy is transferred into the temper when the h2o vapor condenses during the formation of clouds. For instance, think of how a puddle, following a rainstorm, keeps a sidewalk cool until information technology is completely dried past the sunshine. The incoming solar radiation is being used to bulldoze the procedure of evaporation. One time the h2o is gone, the sidewalk begins to absorb solar radiation and heat upwards. If you bear upon the sidewalk with bare feet you tin feel this sensible heat sensible heat: the excess radiative energy that has passed from Earth's surface to the atmosphere through advection, conduction, and convection processes. .
A 2nd mechanism for the redistribution of thermal energy is the process of convection convection: the transfer of thermal free energy by the movement of heated textile from one place to another. , which is the driving strength behind weather. Together, these ii processes account for a significant amount of the Globe'due south radiation budget. In total, free energy leaves Earth's surface through 3 processes: evaporation and condensation (or latent heating and cooling), convection, and emission of thermal infrared radiation. Of these iii processes, 25 percent of the energy that leaves the surface of the Globe is through evaporation and condensation. An additional 5 percent, leaves the surface through convection. As y'all complete the post-obit lab, look for signs of these two important heat transfer processes.
Overview:
In this lab you will build a physical model of the hydrologic, or h2o cycle.
Lab Activeness Instructions
- Set the equipment as show in the effigy, right, or picture beneath.

![[creative commons]](https://serc.carleton.edu/images/creativecommons_16.png)
Provenance: Betsy Youngman, none
Reuse: This item is offered under a Artistic Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike license http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/ You may reuse this particular for non-commercial purposes as long as you provide attribution and offer any derivative works under a similar license. - Cutting a hole large enough to fit the insulated loving cup in the "lid" of your aquarium or articulate plastic shoebox. Or, if you are using plastic wrap, you can just place the ice in a baggie and put information technology directly on the plastic wrap comprehend.
- Add together enough water to fill the container with water to a depth of 2-5 cm. Optional: Add several drops of nutrient coloring to make it easier to encounter the water.
- Position a bag of sand or gravel at i end of the aquarium. The sand / gravel should be in a higher place the water level.
- Add a pocket-sized jar lid or bowl to the "country area" on peak of the sand and under the ice.
- Fill a cup or ziplock handbag with ice and place information technology in the opening in the lid (if using cardboard) or on superlative of the plastic wrap.
- Place a focused lamp, such as a desk lamp, so that it heats the water at the other end of the aquarium or box. If the lid of the box is clear, shine the light through the chapeau; otherwise aim it at the water through the side of the aquarium.
- Plough on the lamp, or identify the appliance in the sun, and scout the water bicycle occur.
One time you have completed this lab answer the Discussion and Stop and Think questions below.
Discuss
Once you have produced your water cycle model, critique its effectiveness and validity. Which parts of the water cycle were clearly demonstrated with this lab and which parts were not well represented? How might y'all document and share your demonstration with other students? Draw a sketch of you water cycle model and add words to describe the processes taking place in the model.
Stop and Think
- Relate each office of your model to the water cycle diagram at the top right of this folio. For case, the lamp represented the lord's day. What other Earth system processes were demonstrated in this lab?
- What was the energy source for the water cycle?
- How does the h2o cycle "transport" energy?
- What exercise you think would happen if you added a 2d or even 3rd lamp?
- Depict what you call up would happen if you left the water bike in a shoebox in the dark for several hours.
Optional Extension
Additional background reading about the h2o cycle and weather can be establish at the following links:
- Water Cycle Article at NASA Earth Observatory
- NOAA Jetstream—background information nearly the water bike and its role in weather and climate.
Source: https://serc.carleton.edu/eslabs/weather/2a.html
0 Response to "what is the source of energy for the water cycle and carbon cycle to occur"
Post a Comment